TL;DR
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) are variables that can affect the production process, directly influencing Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs), which are the key characteristics that ensure product quality. Understanding and controlling CPPs is essential to maintain CQAs within specified limits, ensuring the safety and efficacy of the final product.
Introduction
In the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring product quality and compliance is paramount. Two key concepts integral to this are Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) and Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs).
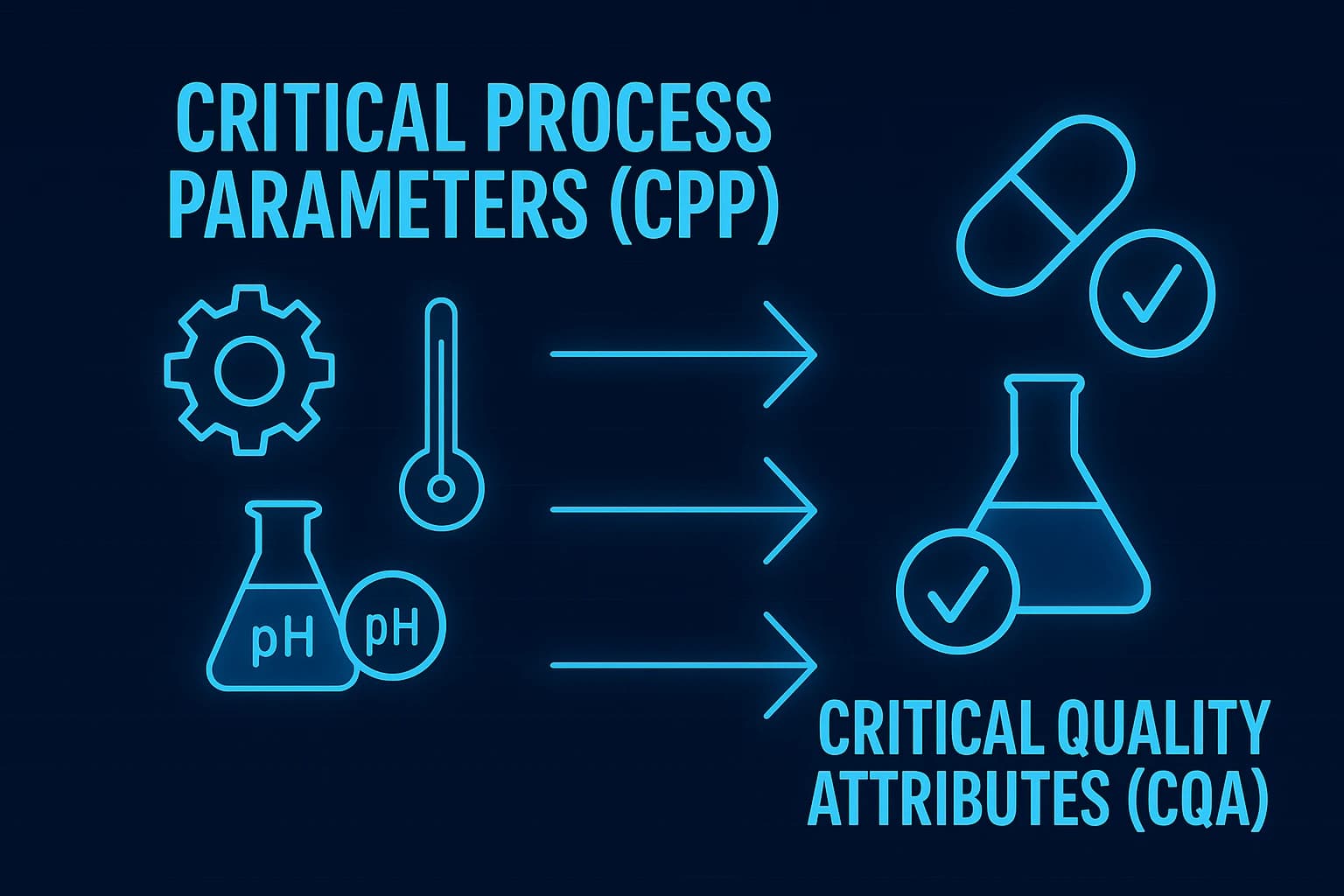
Critical Process Parameters (CPPs)
- Definition: CPPs are variables that can affect the production process and ultimately impact the product's quality.
- Examples: Temperature, pH levels, mixing speed.
- Role: Controlling CPPs is essential to maintain the desired output and prevent deviations that could affect product quality.
Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
- Definition: CQAs are the physical, chemical, biological, or microbiological properties or characteristics that must be within an appropriate limit, range, or distribution to ensure product quality.
- Examples: Purity, potency, stability, dissolution rate.
- Role: CQAs are the benchmarks against which the product is measured to ensure it meets quality standards.
Relationship Between CPPs and CQAs
Interdependence
- Direct Influence: CPPs directly influence CQAs. For instance, a deviation in temperature (a CPP) can affect the potency (a CQA) of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
- Example: If the mixing speed is too slow, it may result in an uneven distribution of the API, affecting the uniformity of dosage units.
Process Control
- Monitoring: By continuously monitoring and controlling CPPs, manufacturers can ensure that CQAs remain within the specified limits.
- Quality Assurance: This practice ensures the final product's safety and efficacy, meeting both regulatory standards and patient needs.
Risk Management
- Identification: Recognizing the relationship between CPPs and CQAs is essential for risk assessment.
- Control Strategies: Implementing appropriate control measures to mitigate potential quality issues ensures compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) and Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) is crucial in pharmaceutical manufacturing. By effectively controlling CPPs, manufacturers can ensure that CQAs meet the required standards, leading to high-quality, safe, and effective pharmaceutical products.
Hashtags
#PharmaIndustry #QualityControl #GMP #ProcessOptimization #PharmaCompliance #CPP #CQA

Practical Guide to 21 CFR Part 11
Your Essential Handbook for Navigating 21 CFR Part 11
"An invaluable resource for anyone working with computerised systems in pharma."
Conor
Quality Assurance
Available on Amazon United Kingdom